Searching for information on Sanitation Workers?
The Sanitation Workers Knowledge + Learning Hub is the best source for all current news, trends, articles and updates on sanitation workers rights around the world.
The Native Medicare Charitable Trust (NMCT), the Bundesministerium für wirtschaftliche Zusammenarbeit (BMZ), the Karl Kübel Foundation (KKF) and the Karl Kübel Stiftung (KKS) organized various programmes due to MHM day celebration. They created a theme for MHM day 2021, which was “Time to celebrate our Womenhood”. Based on the theme they conducted a competition as well as various types of …
WoMena considers positive social norms as an essential component of menstrual health. Therefore, since its beginnings in 2012, WoMena has included community engagement, in particular male engagement, as part of its theory of change and policy. WoMena has also developed a 10-point strategy and reflected this in its monitoring and evaluation (M&E) framework.
Much of the literature on SRHR draws …
Hygiene behaviours in WASH need to be studied from a local context. There is no shortcut to working on behaviour change, without going directly to listen to and observe the reasons for prevailing hygiene practices in the contexts in which these are practised. There is dearth of formativeresearch on hygiene behaviours.
India faces the twin challenges of having the most number of people in the world defecating in the open and also for the burgeoning crisis of untreated fecal waste that is contaminating our surface and ground water creating an imminent health crisis. The latest Swachhta Stats Report1 shows an encouraging 45% rural sanitation coverage by mid 2015 as against the 31% coverage in 2010 Census. Both …
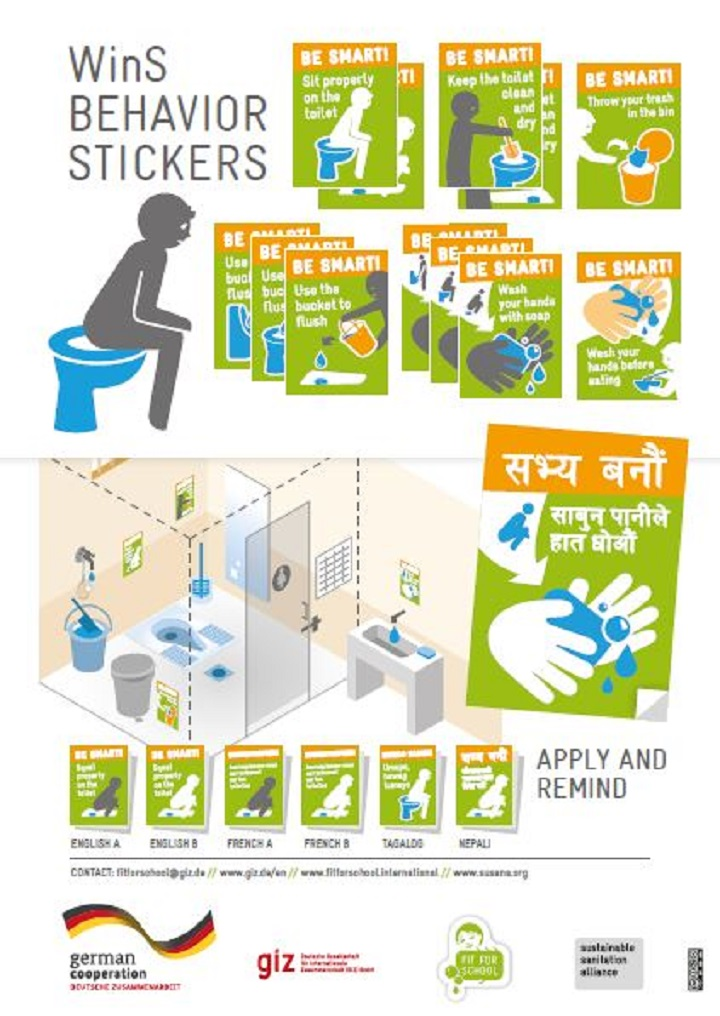
The Ministry of Education and Sports recognizes that Water, Sanitation and Hygiene (WASH) programs in schools (WinS) are a key priority area and that improved hygiene practices and a clean school environment are contributory factors to ensuring that learners can enjoy an acceptable standard of health. The need for a clean school environment is highlighted in the 2016 School WASH mapping report. …
This resource guide by Watson, J. & Drebelbis, R. provides an overview of the science behind nudge-based handwashing interventions and the evidence supporting the use of environmental nudges for handwashing in schools in low-resource settings. Resources and tools for planning and implementing nudge-based interventions in schools are also provided.
Universal access to adequate sanitation is one of the under-appreciated achievements of many societies – and unfortunately remains a distant dream for millions. Even in countries where there is no home without a toilet, public institutions tend to have facilities that are part of the unseen fabric of civilisation. Familiar signs guide the way to public conveniences that are usually open to …
Safe sanitation is essential for health, from preventing infection to improving and maintaining mental and social well-being. The lack of safe sanitation contributes to diarrhoea, a major public health concern and a leading cause of disease and death among children under five years in low- and middle- income countries; poor sanitation also contributes to several neglected tropical diseases, as …
In this report the authors analyse the approaches governments and donors are taking to cross-integrate nutrition and water, sanitation and hygiene (WASH) within their nutrition and WASH national policies and plans. The report aims to provide a ‘recipe’, or toolkit, to stimulate debate and discussion of the options and opportunities to bring together WASH and nutrition policies and programmes.
Water, sanitation and hygiene are essential for preventing and managing diseases including neglected tropical diseases which affect over 1 billion people among the poorest communities. Closer coordination of WASH and NTD programmes is needed to ensure WASH services are reaching the most vulnerable populations. Many WASH and NTD actors have started to work together on the planning and …
Water, sanitation and hygiene (WASH) are critical in the prevention and care for all of the 17 neglected tropical diseases (NTDs) scheduled for intensified control or elimination by 2020.
Provision of safe water, sanitation and hygiene is one of the five key interventions within the global NTD roadmap. Yet to date, the WASH component of the strategy has received little attention and the …
This policy brief highlights the often overlooked opportunity that addressing complementary food hygiene offers the WASH, nutrition and health sectors for improving health outcomes. It outlines SHARE's contribution to narrowing the evidence gap concerning the relationship between food hygiene and child health, indicates opportunities for future research, and offers insights that could influence …
This report, conducted by SHARE and WaterAid, highlights why water, sanitation and hygiene are essential for nutrition. Through an analysis of national nutrition plans and policies in 13 countries, the research highlights the extent to which WASH is embedded at policy level and where and how improvements must be made.
Evidence on Demand was requested by DFID to undertake a rapid desk-based study to assess the level of change in handwashing with soap that could be expected from a successful hygiene promotion intervention in a low or middle-income country setting. As part of this task, a summary of factors that may influence intervention outcomes and
sustainability is provided.
More than 3·5 million children aged less than 5 years die from diarrhoea and acute lower respiratory-tract infection every year. A randomised controlled trial had been undertaken to assess the effect of handwashing promotion with soap on the incidence of acute respiratory infection, impetigo, and diarrhoea.
Diarrhoea and respiratory infections are the two biggest causes of child death globally. Handwashing with soap could substantially reduce diarrhoea and respiratory infections, but prevalence of adequate handwashing is low. Through this research it was tested whether a scalable village-level intervention based on emotional drivers of behaviour, rather than knowledge, could improve handwashing …
The Open Defecation Free (ODF) Malawi 2015 Strategy and National Hand Washing Campaign have been contributing to an increased focus on handwashing with soap (HWWS) in Malawi.1 This is a very positive development!
Some studies estimate that washing hands with soap can reduce diarrhoeal disease rates by up to 50 per cent and respiratory disease rates by up to 25 per cent. This makes handwashing …
In this working paper, we draw on basic scientific findings from psychology, cognitive science, and behavioral economics to propose a framework of 8 System 1 Principles to support the initiation and maintenance of OD behavior change. In doing so, we build from the general framework advanced in the World Bank Group’s (2015) World Development Report: Mind, Society, and Behavior, which emphasized …